What Does It Mean For A Data Warehouse To Be Multidimensional?
Dimensional Modeling
Dimensional Modeling (DM) is a data structure technique optimized for data storage in a Data warehouse. The purpose of dimensional modeling is to optimize the database for faster retrieval of information. The concept of Dimensional Modelling was developed by Ralph Kimball and consists of "fact" and "dimension" tables.
A dimensional model in data warehouse is designed to read, summarize, analyze numeric information like values, balances, counts, weights, etc. in a information warehouse. In contrast, relation models are optimized for add-on, updating and deletion of information in a real-time Online Transaction Organization.
These dimensional and relational models have their unique way of data storage that has specific advantages.
For instance, in the relational way, normalization and ER models reduce redundancy in data. On the contrary, dimensional model in data warehouse arranges data in such a way that it is easier to recollect information and generate reports.
Hence, Dimensional models are used in data warehouse systems and not a good fit for relational systems.
In this tutorial, you lot will learn-
- Elements of Dimensional Data Model
- Fact
- Dimension
- Attributes
- Fact Table
- Dimension Table
- Types of Dimensions in Data Warehouse
- Steps of Dimensional Modelling
- Step ane) Identify the Business Process
- Step ii) Identify the Grain
- Step 3) Identify the Dimensions
- Stride iv) Identify the Fact
- Stride five) Build Schema
- Rules for Dimensional Modelling
- Benefits of Dimensional Modeling
Elements of Dimensional Data Model
Fact
Facts are the measurements/metrics or facts from your business process. For a Sales business organization procedure, a measurement would be quarterly sales number
Dimension
Dimension provides the context surrounding a business process issue. In unproblematic terms, they requite who, what, where of a fact. In the Sales business organization process, for the fact quarterly sales number, dimensions would be
- Who – Customer Names
- Where – Location
- What – Production Name
In other words, a dimension is a window to view data in the facts.
Attributes
The Attributes are the various characteristics of the dimension in dimensional data modeling.
In the Location dimension, the attributes can be
- State
- Country
- Zipcode etc.
Attributes are used to search, filter, or classify facts. Dimension Tables incorporate Attributes
Fact Table
A fact tabular array is a primary table in dimension modelling.
A Fact Tabular array contains
- Measurements/facts
- Foreign key to dimension tabular array
Dimension Table
- A dimension table contains dimensions of a fact.
- They are joined to fact table via a foreign fundamental.
- Dimension tables are de-normalized tables.
- The Dimension Attributes are the various columns in a dimension table
- Dimensions offers descriptive characteristics of the facts with the help of their attributes
- No set limit set for given for number of dimensions
- The dimension can as well incorporate one or more hierarchical relationships
Types of Dimensions in Data Warehouse
Post-obit are the Types of Dimensions in Information Warehouse:
- Conformed Dimension
- Outrigger Dimension
- Shrunken Dimension
- Role-playing Dimension
- Dimension to Dimension Table
- Junk Dimension
- Degenerate Dimension
- Swappable Dimension
- Stride Dimension
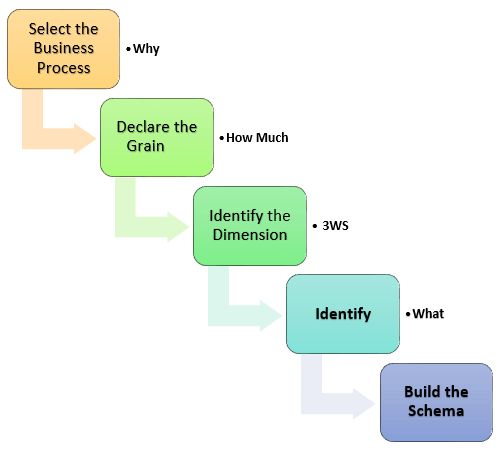
Steps of Dimensional Modelling
The accuracy in creating your Dimensional modeling determines the success of your data warehouse implementation. Here are the steps to create Dimension Model
- Identify Concern Process
- Identify Grain (level of detail)
- Identify Dimensions
- Identify Facts
- Build Star
The model should depict the Why, How much, When/Where/Who and What of your business procedure
Footstep 1) Identify the Concern Process
Identifying the bodily business process a datarehouse should embrace. This could be Marketing, Sales, HR, etc. equally per the data analysis needs of the organization. The pick of the Business organization process likewise depends on the quality of data available for that process. It is the most important step of the Information Modelling process, and a failure hither would have cascading and irreparable defects.
To depict the business process, yous tin use plain text or use basic Business organization Process Modelling Note (BPMN) or Unified Modelling Language (UML).
Step 2) Identify the Grain
The Grain describes the level of detail for the business problem/solution. It is the process of identifying the everyman level of information for any tabular array in your data warehouse. If a table contains sales information for every mean solar day, then it should exist daily granularity. If a table contains full sales data for each calendar month, then it has monthly granularity.
During this phase, yous answer questions like
- Do we need to shop all the available products or just a few types of products? This decision is based on the business processes selected for Datawarehouse
- Practice we store the product auction information on a monthly, weekly, daily or hourly basis? This decision depends on the nature of reports requested by executives
- How do the higher up ii choices affect the database size?
Case of Grain:
The CEO at an MNC wants to discover the sales for specific products in different locations on a daily basis.
So, the grain is "product auction information by location past the day."
Pace iii) Identify the Dimensions
Dimensions are nouns like date, shop, inventory, etc. These dimensions are where all the information should be stored. For example, the date dimension may contain data like a year, month and weekday.
Example of Dimensions:
The CEO at an MNC wants to find the sales for specific products in different locations on a daily ground.
Dimensions: Product, Location and Time
Attributes: For Product: Product cardinal (Foreign Key), Name, Type, Specifications
Hierarchies: For Location: Country, Land, Metropolis, Street Accost, Name
Footstep iv) Place the Fact
This step is co-associated with the business users of the arrangement considering this is where they get access to data stored in the information warehouse. Virtually of the fact table rows are numerical values like price or price per unit, etc.
Example of Facts:
The CEO at an MNC wants to discover the sales for specific products in different locations on a daily basis.
The fact hither is Sum of Sales by product by location by fourth dimension.
Pace 5) Build Schema
In this stride, you implement the Dimension Model. A schema is nothing but the database structure (arrangement of tables). There are ii popular schemas
- Star Schema
The star schema architecture is easy to blueprint. Information technology is called a star schema because diagram resembles a star, with points radiating from a center. The center of the star consists of the fact table, and the points of the star is dimension tables.
The fact tables in a star schema which is third normal form whereas dimensional tables are de-normalized.
- Snowflake Schema
The snowflake schema is an extension of the star schema. In a snowflake schema, each dimension are normalized and connected to more dimension tables.
Also Cheque:- Star and Snowflake Schema in Data Warehouse with Model Examples
Rules for Dimensional Modelling
Post-obit are the rules and principles of Dimensional Modeling:
- Load atomic data into dimensional structures.
- Build dimensional models around business organisation processes.
- Need to ensure that every fact table has an associated date dimension table.
- Ensure that all facts in a unmarried fact table are at the aforementioned grain or level of detail.
- It'due south essential to shop report labels and filter domain values in dimension tables
- Need to ensure that dimension tables utilize a surrogate key
- Continuously residual requirements and realities to deliver business solution to support their controlling
Benefits of Dimensional Modeling
- Standardization of dimensions allows like shooting fish in a barrel reporting across areas of the business concern.
- Dimension tables store the history of the dimensional information.
- Information technology allows to introduce entirely new dimension without major disruptions to the fact table.
- Dimensional also to store data in such a fashion that information technology is easier to call back the information from the information once the information is stored in the database.
- Compared to the normalized model dimensional table are easier to sympathize.
- Information is grouped into clear and simple business organisation categories.
- The dimensional model is very understandable past the business organization. This model is based on business terms, and so that the business organization knows what each fact, dimension, or attribute means.
- Dimensional models are deformalized and optimized for fast information querying. Many relational database platforms recognize this model and optimize query execution plans to assist in operation.
- Dimensional modelling in data warehouse creates a schema which is optimized for high performance. It means fewer joins and helps with minimized data redundancy.
- The dimensional model also helps to boost query performance. It is more than denormalized therefore it is optimized for querying.
- Dimensional models can comfortably accommodate change. Dimension tables tin can accept more than columns added to them without affecting existing business intelligence applications using these tables.
What is Multi-Dimensional Data Model in Data Warehouse?
Multidimensional information model in data warehouse is a model which represents information in the form of data cubes. It allows to model and view the information in multiple dimensions and it is defined past dimensions and facts. Multidimensional data model is generally categorized effectually a key theme and represented by a fact table.
Summary:
- A dimensional model is a information structure technique optimized for Data warehousing tools.
- Facts are the measurements/metrics or facts from your business concern process.
- Dimension provides the context surrounding a business process effect.
- Attributes are the various characteristics of the dimension modelling.
- A fact table is a primary tabular array in a dimensional model.
- A dimension table contains dimensions of a fact.
- There are three types of facts 1. Condiment ii. Not-additive 3. Semi- additive .
- Types of Dimensions are Conformed, Outrigger, Shrunken, Role-playing, Dimension to Dimension Table, Junk, Degenerate, Swappable and Step Dimensions.
- Five steps of Dimensional modeling are 1. Identify Business Process 2. Identify Grain (level of detail) 3. Identify Dimensions 4. Identify Facts 5. Build Star
- For Dimensional modelling in data warehouse, at that place is a need to ensure that every fact table has an associated date dimension tabular array.
What Does It Mean For A Data Warehouse To Be Multidimensional?,
Source: https://www.guru99.com/dimensional-model-data-warehouse.html
Posted by: mazurfident75.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Does It Mean For A Data Warehouse To Be Multidimensional?"
Post a Comment